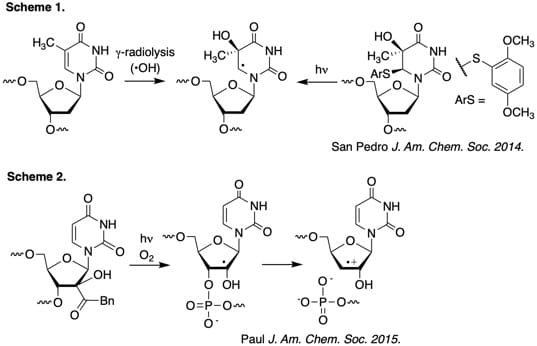
DNA damage by agents such as g-radiolysis and many antitumor antibiotics involves the formation of radical intermediates (Scheme 1). Oxidative RNA (Scheme 2) damage is important in neurological diseases and in studies on RNA structure/folding. We use organic chemistry to independently synthesize putative reactive intermediates at defined sites in oligonucleotides to address fundamental chemical questions concerning how nucleic acids are oxidatively damaged. The reactivity of these biologically important species is determined using a variety of tools that include isotopic labeling, electrospray and MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry, kinetics, enzymes, and molecular modeling.
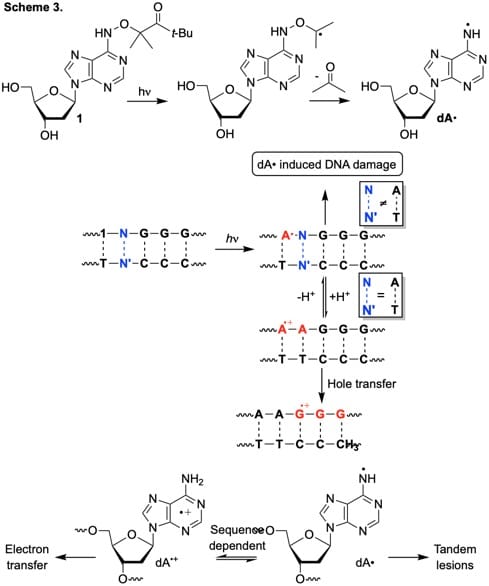
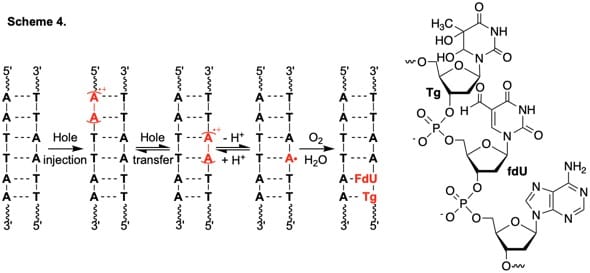
Using this approach we have resolved mechanistic controversies and discovered novel nucleic acid damage pathways. For instance, we recently independently generated a purine radical for the first time in DNA. This enable us to determine that the direct and indirect effects of gamma-radiolysis converge in a sequence dependent manner (Scheme 3). We also were able to resolve how nucleic acids are oxidatively damaged in poly(dA-T) sequences (Scheme 4).
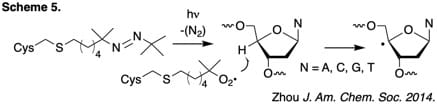
Finally, we have applied this approach to studying DNA damage in nucleosome core particles by independently generating protein radicals in engineered histones (Scheme 5).
For relevant publications see:
•5.6-Dihydropyrimidine Peroxyl Radical Reactivity in DNA. San Pedro, J. M. N.; Greenberg, M. M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 3928-3936. (PMC: 3980663)
• DNA Damage by Histone Radicals in Nucleosome Core Particles. Zhou, C.; Greenberg, M. M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 6562-6565. (PMC: 4017609)
• Rapid RNA Strand Scission Following C2′-Hydrogen Atom Abstraction. Paul, R.; Greenberg, M. M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 596-599.
• DNA Damage Emanating From a Neutral Purine Radical Reveals the Sequence Dependent Convergence of the Direct and Indirect Effects of -Radiolysis. Zheng, L.; Greenberg, M. M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 17751-17754. (PMC: 5729073)
• Traceless Tandem Lesion Formation in DNA From a Nitrogen-Centered Purine Radical. Zheng, L.; Greenberg, M. M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 6400-6407. (PMC: 5966344)
• Independent Generation of Reactive Intermediates Leads to an Alternative Mechanism for Strand Damage Induced by Hole Transfer in Poly•(dA-T) Sequences. Sun, H.; Zheng, L.; Greenberg, M. M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 11308-11316. (PMC: 6135700)