“All we have discovered is that it starts with a single individual – always a child – and then spreads explosively, like the formation of crystals round the first nucleus in a saturated solution.” Arthur C. Clarke (Childhood’s End, 1953)
To process your request, an application form must be submitted for each individual sample. Our X-ray facility operates on a first-come, first-served basis (with exceptions possible in special cases). When submitting samples, please remember:
>>> GOLDEN RULE: IT IS ALWAYS BEST TO KEEP YOUR CRYSTALS IN THE MOTHER LIQUOR/SOLVENT!!! <<<
This practice prevents crystal decomposition (particularly when the crystal lattice contains solvent molecules) and makes it easier to select intact crystals from the batch, thereby reducing the risk of damage.
The procedure to follow is outlined below:
1. Download the submission form – doc | pdf.
2. Complete the form with all required information about your sample (all fields are important).
3. Submit the form by either:
(i) Printing a copy and including it with your sample, or
(ii) Emailing it to [email protected]
Each sample is first examined under a stereomicroscope for a preliminary assessment. If crystals are present, a small portion is transferred onto a microscope slide with Parabar 10312 (oil) and inspected under cross-polarized light. Crystals are most often single, though twinning is also common. When twin domains are clearly visible, microsurgery can usually separate the individual domains with little effort—though this is more challenging with plate-like crystals. Even when crystals appear to be of good quality (e.g., large size, well-defined faces, sharp edges, smooth surfaces), the final step of the preliminary evaluation is to collect a few diffraction frames. High-quality crystals are identified by sharp, unsplit reflections across both low and high resolution (unless the crystals are merohedrally twinned).
 Crystals of poor quality |
 Crystals of good quality |
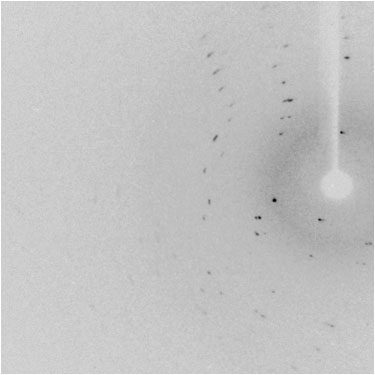 Diffraction pattern of poor quality |
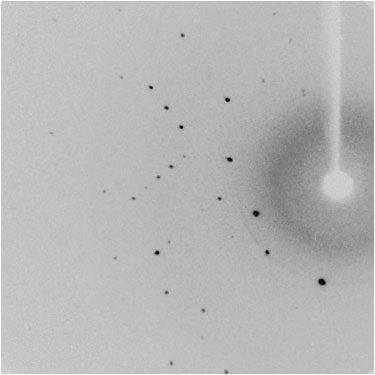 Diffraction pattern of good quality |
ZIP Package
Upon completion of the X-ray structure determination, you will receive a zip archive via email. For straightforward structures, the archive is typically sent within the same day (or might take 1–2 business days), while more complex cases might possibly require several days. A preliminary plot or preliminary .res file illustrating the chemical connectivity may also be provided within the first day of data collection.
Each structure is assigned a unique code, which follows the format xs####a or XR####a, depending on whether the data were collected on the Rigaku SuperNova or the Rigaku XtaLAB Synergy-R system. The corresponding zip archive is named either xs####a.zip or XR####n.zip.
When the zip file is extracted, a main directory (xs####a or XR####a) is created. This directory tyically contains eight subdirectories, each serving a specific purpose:
- xs(XR)####a/cif_final
Contains the file xs(XR)####a_final.cif. This CIF (Crystallographic Information File) includes all essential information related to the crystal structure and experimental data. This file must be submitted along with your manuscript to the target journal. Some journals require prior deposition of CIF files with the CCDC; if so, please follow [this link] for instructions. - xs(XR)####a/crystal_morphology
Contains two digitized photographs of the crystal (mounted on the mounting pin) used for data collection. - xs(XR)####a/experimental_report
Contains two files: experimental.cif, which provides general information about data collection (this file should not be submitted with your manuscript), and experimental.doc, the corresponding report file. - xs(XR)####a/invoice_copy
Contains the issue receipt (PDF file). - xs(XR)####a/ortep
Contains one displacement ellipsoid plot (typically given at the 50% probability level) of the compound of interest. These are generally generated with Mercury. - xs(XR)####a/platon_report
Contains the files (c)x####n.chk (CIF validation) and (c)x####n.ckf (FCF validation), both generated by PLATON. These files are primarily useful for crystallographers but could still be relevant for chemists. - xs(XR)####a/precess
Contains six digitally reconstructed precession photographs (0kl, 1kl, h0l, h1l, hk0, and hk1). These images are typically used to evaluate the quality of the crystal, check for systematic absences, confirm lattice symmetry, and identify potential issues such as twinning or diffuse scattering. - xs(XR)####a/refin
Contains all files required for structure refinement (e.g., .res and .hkl files). These files store the refined atomic model and the reflection data, respectively, and are essential if the structure needs to be re-refined, modified, or validated in the future.
